Deionised water, often abbreviated as DI water, is a type of purified water that has had most of its mineral ions removed. This process results in water with very low electrical conductivity, making it ideal for various industrial and scientific applications. But what exactly is deionisation, and how does it differ from other water purification methods? This comprehensive guide delves into the world of deionised water, exploring its creation, and applications, and even answering some frequently asked questions.
Demystifying Deionisation: What is Deionised Water?
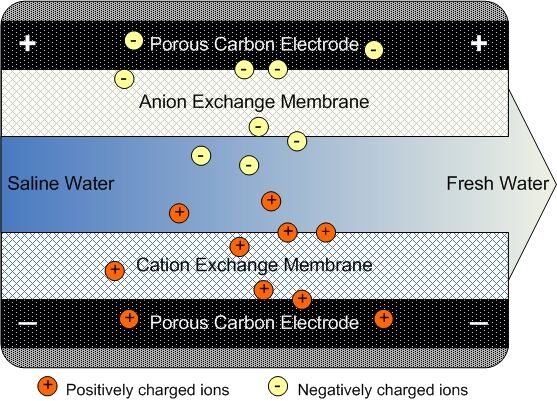
Deionised water is essentially water stripped of its mineral ions. These ions, typically composed of dissolved salts and minerals like calcium, magnesium, and sodium, are removed through a process called deionisation. This process utilises ion exchange resins, which act like tiny magnets selectively attracting and holding onto charged particles (ions) present in the water. As the water flows through these resins, the ions are trapped, leaving behind purer water with minimal electrical conductivity.
How is Deionised Water Made?
The deionisation process typically involves two main stages:
- Pre-treatment: Before reaching the ion exchange resins, the water often undergoes pre-treatment. This pre-treatment stage may involve processes like filtration and reverse osmosis to remove larger particles, impurities, and organic materials that could clog the resin beds or interfere with the deionisation process.
- Deionisation: Once pre-treated, the water passes through tanks containing ion exchange resins. These specialised resins contain positively and negatively charged beads that attract and capture oppositely charged ions from the water. As the water flows through the resin beds, the ions are removed, leaving behind demineralised water.
Weighing the Pros and Cons:
Advantages and Disadvantages of Deionised Water
While deionised water offers several benefits, it’s crucial to understand its limitations as well.
Advantages of Deionised Water
- High purity: Free from most mineral ions, ideal for applications requiring high purity water
- Low electrical conductivity: Excellent insulator, making it suitable for various electrical applications.
- Extends shelf life of products: Inhibits bacterial growth due to the absence of minerals, extending the shelf life of certain products.
Disadvantages of Deionised Water
- Not suitable for drinking: Lack of minerals can make it taste bland and potentially leach minerals from the body with prolonged consumption.
- Can be corrosive to certain metals: Due to the absence of minerals that can form a protective film, deionised water can be slightly corrosive to some metals.
- Requires specific storage and handling: Deionised water readily absorbs carbon dioxide from the air, impacting its pH and conductivity.
Finding the Right Fit: When is Deionised Water Used?
Deionised water plays a crucial role in various industries:
- Used in cleaning and rinsing electronic components due to its high purity and low conductivity.
- Pharmaceuticals and medical applications: Essential for preparing pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and solutions requiring high purity.
- Chemical and automotive industries: Employed in various processes requiring pure water, such as battery production and coolant systems.
- Laboratories: A staple in scientific research and analysis due to its minimal interference with experiments.
Addressing Common Concerns: FAQs about Deionised Water
Here are some frequently asked questions about deionised water:
- Is deionised water the same as distilled water?No, while both are forms of purified water, they differ in the purification process. Distillation involves boiling water and collecting the vapor, leaving behind contaminants in the boiling chamber. Deionisation, on the other hand, uses ion exchange to remove charged particles without changing the water’s physical state.
- Is it safe to drink deionised water?While deionised water is generally safe for occasional consumption, it’s not recommended as a primary source of hydration. The lack of minerals can alter the taste and potentially lead to mineral deficiencies with prolonged consumption.
- How long does deionised water last?Deionised water can last for an extended period if stored properly in airtight containers. However, it is susceptible to absorbing carbon dioxide from the air, which can slightly alter its pH and conductivity. For critical applications, it’s recommended to use freshly deionised water.
Next Steps: Explore the Benefits of Deionised Water
Whether you’re working in a scientific research lab or require high-purity water for specific industrial applications, deionised water provides a valuable solution. With its unique properties and diverse uses, deionised water plays a significant role in various sectors.
**If you’re looking for a reliable source of deionised water for your specific needs, Wychwood Water offers a range of high-quality deionisation systems and services. We understand the critical nature of water purity in various applications and are dedicated to providing customised solutions to meet your specific requirements. Contact our water specialists today to discuss your needs and explore how Wychwood Water can help you access the power of deionised water.
To find out more about how we could help you recycle your water, including the designing, manufacturing, installing & commissioning, servicing, and refurbishment of water purification systems, request a Free consultation to find the commercial water treatment solution you’ve looking for.